把计数器的值保存到 .aux 文件里。
\documentclass{article}
\makeatletter
% 保存那些要记录的计数器,它值的格式为 \ysk@savecurrcounter{counter1}\ysk@savecurrcounter{counter2}...
\newcommand{\ysk@totalcounters}{}
\AddToHook{enddocument/afterlastpage}{\ysk@totalcounters} % 所有页面都已经输出,但.aux文件还未关闭
\newcommand\ysk@settotalcounter[2]{\global\@namedef{total#1s}{#2}} % 在.aux文件内执行
% 这个命令放在 \ysk@totalcounters 里,由它实际保存计数器的最后一个值
\protected\def\ysk@savecurrcounter#1{\immediate\write\@auxout
{\string\ysk@settotalcounter{#1}{\number\value{#1}}}}
% 这个命令负责初始化并且全局地为 \ysk@totalcounters 添加新值
\newcommand{\ysk@initandaddtocounter}[1]{%
\ysk@settotalcounter{#1}{0}% 先暂时定义,以避免.aux不存在时出错
\xdef\ysk@totalcounters{\ysk@totalcounters\ysk@savecurrcounter{#1}}}
\NewDocumentCommand{\DeclareTotalCounters}{ >{\SplitList{,}} m } % 接受一个逗号分隔的列表
{\ProcessList{#1}{\ysk@initandaddtocounter}}
% \DeclareTotalCounters 只能用于导言区,\AtBeginDocument(begindocument 钩子)中也不行
\AddToHook{begindocument/before}{\RenewDocumentCommand{\DeclareTotalCounters}{m}{\ERROR}}
\makeatother
\newcounter{yskcount}
\newcounter{foocount}
\DeclareTotalCounters{yskcount,foocount}
\begin{document}
Total yskcount: \totalyskcounts.
Total foocount: \totalfoocounts.
\setcounter{yskcount}{9}
\stepcounter{yskcount} % yskcount=10
\setcounter{foocount}{42} % foocount=42
\end{document}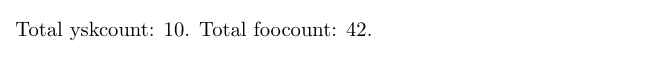
另外,参加 totalcount 和 xassoccnt 宏包。





问 如何定义一个命令,使得这个命令能够储存某个计数器的最后一个值,并在需要的位置将其储存的值释放出来?