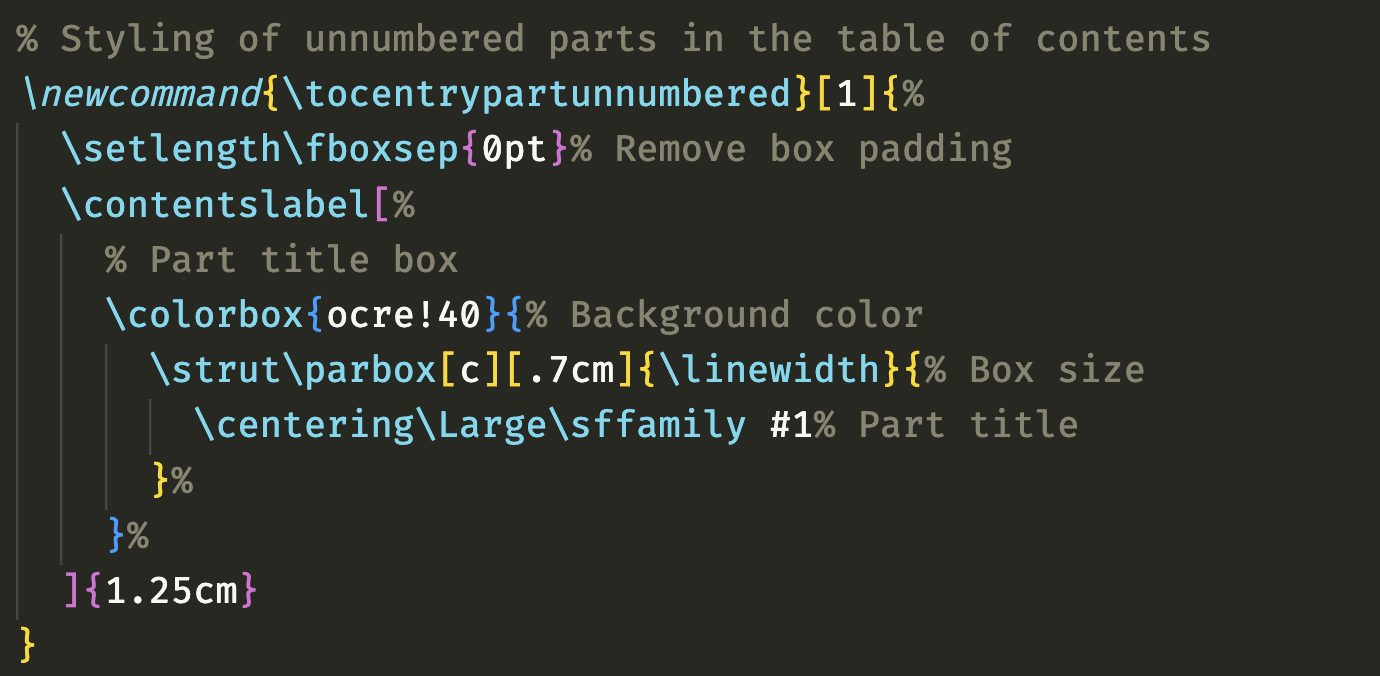
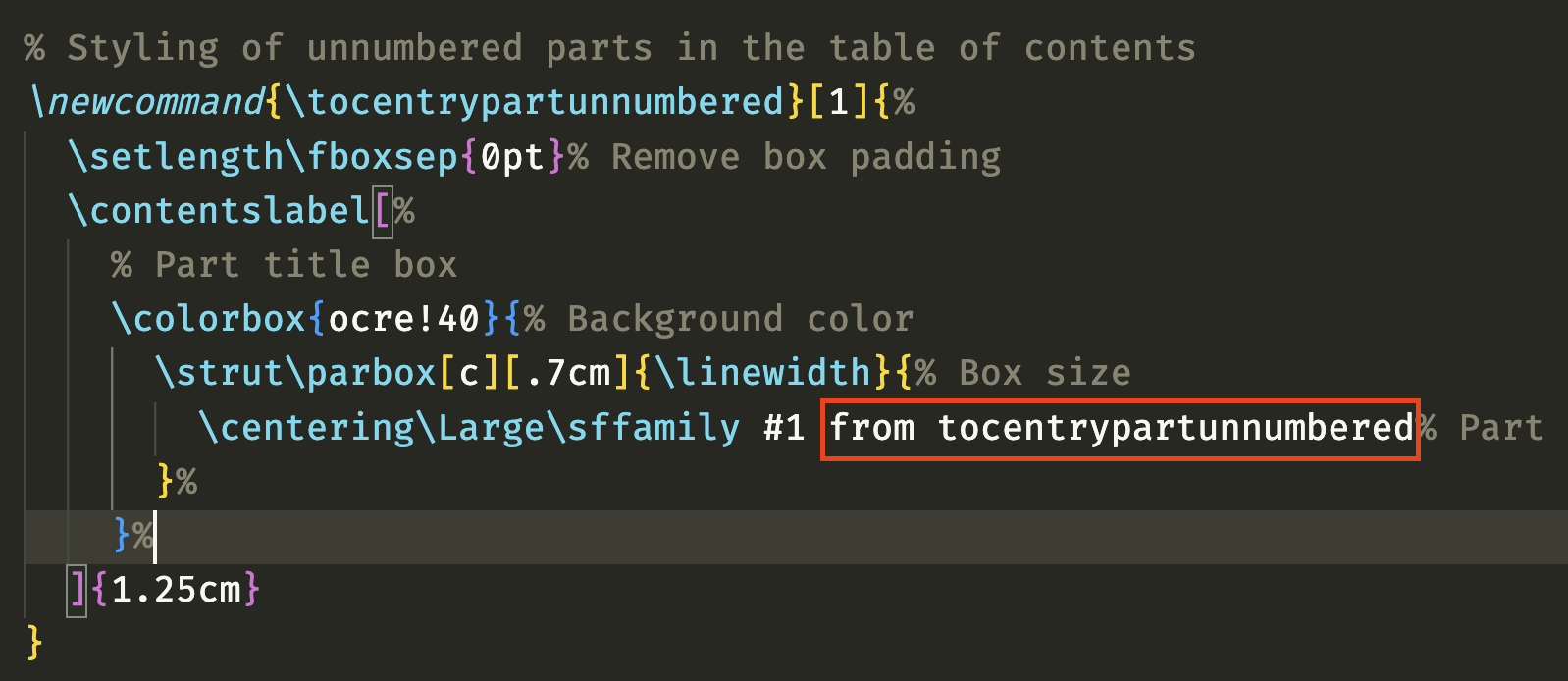
1.如果对所有url都统一显示“点此访问”:
\usepackage[hidelinks]{hyperref}
\DeclareFieldFormat{url}{\href{#1}{[点此访问]}}2.如果对不同的条目有客户化需求,可以利用现有的暂时没用上的字段来存储需要显示的内容,比如titleaddon:
@Online{ctex2022,
% eprint = {点此访问:},
% eprinttype = {github},
title = {CTEX 宏集手册},
author = {CTEX.ORG},
date = {2022-07-14},
url = {https://github.com/CTeX-org/ctex-kit},
titleaddon = {abc}
}
@Online{xecjk2022,
% eprint = {点此访问:},
% eprinttype = {CTAN},
title = {xeCJK 宏包},
author = {CTEX.ORG},
date = {2022-08-06},
url = {https://ctan.org/pkg/xecjk},
titleaddon = {xyz}
}\DeclareFieldFormat{url}{%
\iffieldundef{titleaddon}
{\href{#1}{[点此访问]}} % 如果 titleaddon 为空,显示默认文字
{\href{#1}{[\strfield{titleaddon}]}} % 如果不为空,显示 titleaddon 的内容
}
\DeclareFieldFormat{titleaddon}{}

















问 如何使用 biblatex 把在线资源的 url 文本变成指定文本?